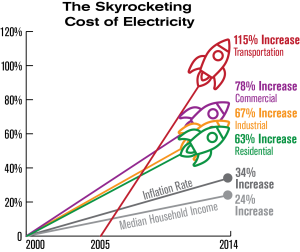
Nowadays, the world is encountering an energy emergency because of restricted assets and enormous energy requests. Thus, a substitute strategy for producing power is vital. One innovation called Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC) is created. To produce power, this innovation utilizes microorganisms to change over synthetic energy into electrical energy. After many investigations and joint efforts, it is realized that losses from the microorganisms are likewise utilized including a wide exhibit of carbon sources to deliver power- best energy plans in Houston .
Kinds of Microbial Fuel Cell
There are two kinds of MFC innovation, which are without arbiter and go between types.
Mediator Free Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC)
This sort of MFC utilizes microorganisms that are bio electrochemically enacted for the exchange of the electrons to a cathode. It contains electrochemical dynamic redox compounds like cytochromes, which are available on the external film and help in moving electrons.
The biofilm structures on the outer layer of the anode chamber give direct electron movement by conductance to the anode. The instances of bio-electrochemically dynamic microscopic organisms utilized in this kind are Aeromonas hydrophila and Shewanella putrefaciens.
Mediator Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC)
This kind of MFC is electrochemically inert. That implies the microorganisms in the fuel can’t move the electrons with no help from a middle person like humic corrosive. Middle people utilized in this kind are unfortunate, harmful, and costly. The arbiter decreases the oxidizing state by catching the electrons and moving them to the anode for the reoxidation interaction. This type is most regularly utilized in research centers.
Different sorts of microbial fuel cells are,
- Microbial Electrolysis Fuel Cell (MEFC)
- Soil-based MFC
- Phototrophic Biofilm MFC
- Nanoporous MFC
- Dregs MFC
- Layer less MFC
- Parts Of Microbial Fuel Cell
There are different parts of the microbial fuel cell, which are significantly partitioned into 2 chambers. They are an anodic chamber and a cathodic chamber. The anodic chamber contains the anode and the cathodic chamber contains the cathode. A few parts of the microbial fuel cell are examined in this segment.
- Anode chamber
- Cathode chamber
- Trade layer
- Substrate
- Electrical circuit.
- Organisms or Microorganisms
- Terminals and copper wires for interfacing cathodes.
Anode Chamber
It is a biocompatible and conductive part, which is steady synthetically with the substrate. The microscopic organisms present in this chamber convert the substrate to H2O (water), CO2 (carbon dioxide), and energy. These microbes are put away in a climate with restricted oxygen levels. It is comprised of a treated steel network with graphite bars or plates.
Cathode Chamber
In this chamber, the protons and electrons are recombined. The degree of oxygen (O2) is decreased in water. It involves Pt as an impetus.
Trade Layer
It goes about as either a cation trade layer or a proton trade film. The trade layer in MFC innovation utilizes Ultrex or Nafion. The protons are permitted to course through this film. While on the opposite side, the electrons and protons are recombined.
Electrical Circuit
The electrons leave the anode chamber and travel through the electrical circuit to supply the power to the stack.
Substrates
These are utilized to produce energy for the microbe’s cell. The power thickness, Coulombic productivity, execution, and financial feasibility of a microbial fuel cell are impacted by the sort of substrate utilized. The natural substrates, which can be utilized in MFC are protein, unpredictable acids, carbs, wastewater, and cellulose. The most regularly utilized substrate is Acetic acid derivation.
Microorganisms
The microorganisms or microorganisms utilized in the MFC innovation depend on the way of life of the microbes.
1). Axenic microorganisms
- Metal that lessens microorganisms
- Geobacter sulfurreducens
- Rhodoferax ferrireducens
- Clostridium beijerinckii
- Shewanella putrefaciens.
2). Blended bacterial fuel
- Alcaligenes faecalis
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Enterococcus faecium
- Proteobacteria
- Desulfuromonas
- Clostridium butricum
- Bacteroides
- Nitrogen-fixing microorganisms like Azospirillum and Azoarcus
- Aeromonas species